Is this not what you were looking for? Switch to the current version or choose one from the drop-down menu.
2 Proxy load balancing and high availability
Overview
Zabbix proxies can be organized into proxy groups to enable proxy load balancing and high availability.
Proxy load balancing and high availability is the automatic redistribution of hosts between proxies within a proxy group:
- If a proxy goes offline, its hosts will be moved to other proxies, thus maintaining high proxy availability.
- If a proxy has a much higher/lower number of hosts than other proxies, its hosts will be moved to other proxies to balance proxy load.
Host redistribution works only between proxies in a group that meet the following conditions:
- Proxies are running Zabbix 7.0 or later.
- Proxy version matches Zabbix server version. If using Zabbix agent (passive), proxy version must match agent version. Active agents only require Zabbix 7.0 or later.
- The proxy group has an online state.
- Hosts are configured to be monitored by a proxy group rather than by individual proxies.
Proxy group health can be monitored with internal checks by any host assigned to a proxy group. However, to monitor the health of a single proxy in a group, assign the host to that proxy; otherwise, results may be inconsistent.
Host redistribution
Proxy load balancing and high availability is managed by Zabbix server via the proxy group manager, which continuously monitors the state of all proxies in each proxy group and their host distribution.
Proxy high availability within a group is ensured via proxy failover: when a proxy goes offline, its hosts are immediately redistributed to other proxies. Proxy load balancing also occurs, as hosts are reassigned to proxies with the fewest assigned hosts.
Additionally, proxy load balancing is triggered when proxy host count differs from the group average by at least 10 hosts and a factor of 2 (host excess or host deficit). If the imbalance persists after a grace period (10 x failover delay), the proxy group is queued for host redistribution.
The proxy group manager redistributes hosts using the following logic:
- Calculate the average number of hosts per proxy.
- For proxies with host excess—move the excess hosts to the unassigned pool of proxies.
- For proxies with host deficit—calculate how many hosts are needed to reach balance.
- Remove the required number of hosts from proxies with the most hosts.
- Move unassigned hosts to proxies with the fewest hosts.
Examples of host redistribution:
| Hosts on proxy | Group average | Host reassignment |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 50 | Yes |
| 60 | 50 | No |
| 40 | 50 | No |
| 25 | 50 | Yes |
| 15 | 5 | Yes |
| 10 | 5 | No |
Having fewer than 10 hosts monitored by a proxy group may lead to uneven host distribution among proxies in the group.
Configuring a proxy group
To configure a proxy group in Zabbix frontend:
- Go to Administration > Proxy groups
- Click Create proxy group
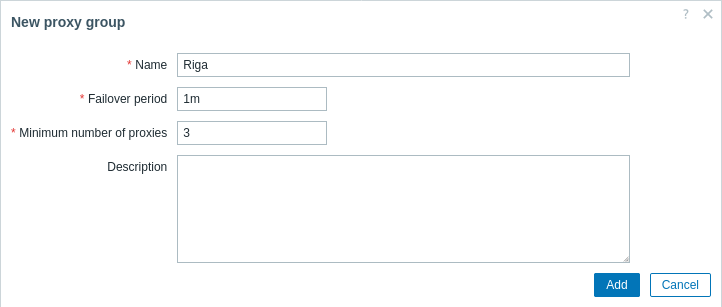
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the proxy group. |
| Failover period | Period in seconds during which a proxy in the proxy group must communicate with Zabbix server to be considered online (default: 1m; range: 10s–15m). If the proxy does not communicate within this period, the proxy state is changed to Offline, and its hosts are immediately redistributed to other proxies. Proxy load balancing begins after 10 x this period. Supports time suffixes (e.g., 30s, 1m) and user macros. |
| Minimum number of proxies | Minimum number of online proxies required to keep the proxy group online (default: 1; range: 1–1000). Supports user macros. This value should be less than the total number of proxies in the group. For example, in a group of 10 proxies, setting the minimum to 10 will cause the group to go offline if any proxy fails. Note that online proxies in an offline group continue to function normally, but load balancing/high availability will not take place. |
| Description | Description of the proxy group. |
| Proxies | Displays a list of up to five proxies (as links or in plain text, depending on user permissions to proxies) when editing a group with proxies. |
Configuring proxy load balancing
To use proxy load balancing, you need to configure a proxy group in Zabbix frontend (see above) and make sure that hosts are monitored by a proxy group, not individual proxies (you may use host mass update to move hosts from proxies to the proxy group).
If using Zabbix agent, also configure it as follows:
- For passive checks, list all proxy group proxies in the Server parameter.
- For active checks, it's recommended to list all proxy group proxies or Zabbix server in the ServerActive parameter. Note that only Zabbix agent 7.0 (or later) will work with proxy groups in its active mode.
If the ServerActive parameter includes only one proxy from a proxy group (or Zabbix server), the agent will still be able to connect to the correct proxy. When the agent service starts and connects to the specified proxy, the agent will receive and cache the full list of proxy IPs and their current load within the group. Then, active checks will be redirected to the correct online proxy for the host, based on the current proxy-host assignment within the proxy group.
Having only a single proxy specified in Zabbix agent ServerActive parameter may lead to lost monitoring data if the agent is started/rebooted while the specified proxy is offline.
When using Zabbix sender, data requests are also redirected to the correct online proxy for the host, based on the current proxy-host assignment within the proxy group. However, if you're sending values of multiple hosts from an input file, use the -g option to prevent sending data to the wrong proxy.
Zabbix agent must also be able to connect to all proxies in the proxy group through the firewall. Otherwise, active checks may hang or fail during redirection or failover. For example:
- During active checks, a proxy may redirect the agent to another proxy. If that proxy is blocked by a firewall, the communication will hang while waiting for a response.
- In stable high-availability setups without recent rebalancing, agents may never contact backup proxies. If firewall rules changed and weren't tested, failover may fail.
Testing proxy load balancing
To test proxy load balancing:
- Configure a proxy group.
- Make sure that the proxy group has an online state.
- Make sure that hosts are monitored by a proxy group, not individual proxies (you may use host mass update to move hosts from proxies to the proxy group).
- Wait a few seconds for the configuration update and host distribution among proxies in the proxy group. Observe the change by refreshing the host list in Administration > Proxies.
Important notes
- SNMP traps are not supported by proxies in proxy group.
- Checks that depend on external configuration (e.g., scripts for external checks or ODBC configuration for database checks) must have the same configuration on all proxies in proxy group.
- Database checks require extended permissions on the database object/server.
- VMware hosts monitored by a proxy group will be randomly spread between proxies in the group. This causes each proxy to cache all VMware data, resulting in additional load on vCenter.
- Hosts created based on autoregistration data from a proxy in a proxy group are set to be monitored by that proxy group. However, hosts created based on network discovery data from a proxy in a proxy group are set to be monitored by that proxy.

